Brain: Part of the central nervous system. It contained within the cranium.
Cerebrum: The largest portion of the brain, left and right hemispheres, controls muscles, interprets general senses, sight & hearing, intellect, memory, and emotional reactions.
Ventricles: spaces filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Cerebellum: assist in the coordination of skeletal muscles & maintain balance.
Brainstem: Connects the brain with the spine.
Pons: It is an essential part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum and brainstem and acts as a control center.
Medulla oblongata: Contains centers that control respiration, heart rate, and the muscles in the blood vessel walls.
Spinal cord: Passes through the vertebral canal, conducts nerve impulses, initiates reflex action to sensory information without input from the brain.
 |
| Spinal Cord |
Meninges: Three membranous layers (dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater) that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Dura mater: It is a thick and tough membrane outer layer of the meninges(brain and spinal cord).
Arachnoid mater: Delicate the middle layer of the meninges.
Pia mater: Thin inner layer of the meninges.
Nerve cell: It is a Cord-like structure also known as neurons. It carries impulses from one part of the body to another. There are 12 cranial nerves, 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
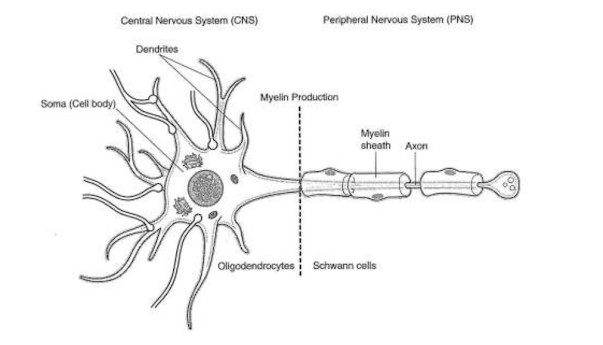 |
| Nerve cell |
Ganglion: Group of nerve cells located in the peripheral nervous system.
Cerebellitis: Inflammation of the cerebellum.
Cerebral thrombosis: Clot in the cerebrum.
Duritis: Inflammation of the dura mater.
Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain.
Encephalomalacia: Softening of the brain.
Meningitis: Inflammation of the meninges.
Neuralgia/Neurodynia: Pain in a nerve.
Neuritis: Inflammation of the nerve.
Neuroma: Neoplasm derived from cells of the nervous system
Poliomyelitis: It is also known as gray matter myelitis, inflammation of the gray matter of the spinal cord due to infection.
Radiculitis: Inflammation of the nerve roots.
Subdural hematoma: Due to injury collection of blood or blood tumor below the dura matter.
Alzheimer’s disease: A progressive degenerative disease of the brain that causes impairment of memory and dementia manifested by confusion, loss of recognition of a person or familiar surroundings, visual-spatial disorientation, inability to calculate, and deterioration of judgment, and restlessness.
Bell’s palsy: Temporary one side facial paralysis or weakness.
Cerebrovascular accident: Interruption of blood supply to the brain caused by cerebral thrombosis, embolism, or hemorrhage.
Epilepsy: Recurring seizures.
Parkinson’s Disease: Brain disorder -a chronic degenerative disease of the CNS.
Symptoms include muscular tremors, rigidity, expressionless face, and shuffling gait.
Psychosis: Mental disorder, extreme derangement often with delusions and hallucinations.
Sciatica: Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, causing pain from the thigh to the foot and toes.
Transient ischemic attack: Inadequate supply of blood to the brain for a short time.TIA is a warning sign of a Stroke.
Ganglionectomy: Excision of a ganglion.
Neurectomy: Excision of a nerve.
Neurolysis: Destruction of nerve tissue.
Neuroplasty: Surgical repair of a nerve.
Neurotomy: Incision into a nerve.
Cerebral angiography: Taking X-ray-of the blood vessels of the brain.
Myelogram: X-ray film of the spinal cord.
Echoencephalography: Process of recording the brain by use of sound.
Electroencephalogram/EEG: Record and evaluate the electrical activity of the brain. With the instrument Electroencephalograph and the process of recording is Electroencephalography.
Lumbar puncture: Insertion of a needle into the subarachnoid space to remove CSF for diagnostic purposes.
Anesthesia: Loss of feeling or sensation.
Cephalalgia/Headache: Pain in the head.
Dysphasia: Difficulty speaking.
Hemiparesis: Paralysis of half of the body.
Hyperesthesia: Excessive sensitivity.
Monoparesis: Slight paralysis of one limb.
Monoplegia: Paralysis of one limb.
Neurologist: A physician who specializes in Neurology
Neurology: Branch of medicine that deals with the nervous system’s function and disorders.
Psychiatry: Branch of medicine that deals with the treatment of mental disorders.
Psychologist: Specialist in the study of Psychology.
Psychiatrist: A physician who treats mental disorders.
Quadriplegia/Tetraplegia: Paralysis of four limbs.
Ataxia: Lack of muscle coordination.
Cognitive: Concerning the mental process of comprehension, judgment, memory, and understanding.
Coma: State of profound unconsciousness.
Conscious: Awake, alert, aware of one’s surroundings.
Unconsciousness: State of being unaware and incapable of responding to stimuli.
Convulsion/Seizure: Sudden involuntary contraction of a group of muscles OR a violent spasm or series of jerkings of the face, trunk, or extremities.
Dementia: Mental decline.
Disorientation: A nature of mental confusion as to time, place, or identity.
Gait: Manner or style of walking.
Incoherent: Inadequate to express one’s thoughts or concepts in an exact, intelligible manner.
Paraplegia: Paralysis of both lower extremities and, generally, the lower trunk, caused by damage to the spinal cord.
Syncope: LOS(loss of consciousness) and postural tone due to diminished cerebral blood flow.
Reflex: A reflection. An involuntary reaction in response to a stimulus applied to the periphery and transmitted to the nervous centers of the brain or spinal cord.
Dementia: Mental decline.
Disorientation: A nature of mental confusion as to time, place, or identity.
Gait: Manner or style of walking.
Incoherent: Inadequate to express one’s thoughts or concepts in an exact, intelligible manner.
Paraplegia: Paralysis of both lower extremities and, generally, the lower trunk, caused by damage to the spinal cord.
Syncope: LOS(loss of consciousness) and postural tone due to diminished cerebral blood flow.
Reflex: A reflection. An involuntary reaction in response to a stimulus applied to the periphery and transmitted to the nervous centers of the brain or spinal cord.
Sense Organ – Eyes
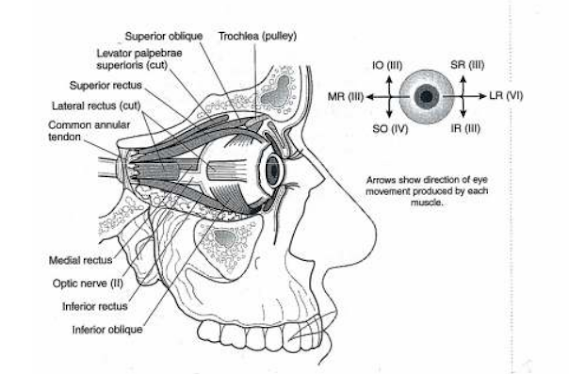 |
Muscle of Eye |
Sclera: Outer protective covering of the eye.
Cornea: Transparent anterior part of the sclera.
Choroid: Middle layer of the eye.
Iris: Muscular structure that gives the eye its color, allows light to pass through.
Pupil: Opening in the center of the iris.
Lens: Behind the pupil, focus, and bend light.
Retina: Innermost layer, contains the vision receptors.
Aqueous fluid: Watery liquid found in the interior cavity of the eye.
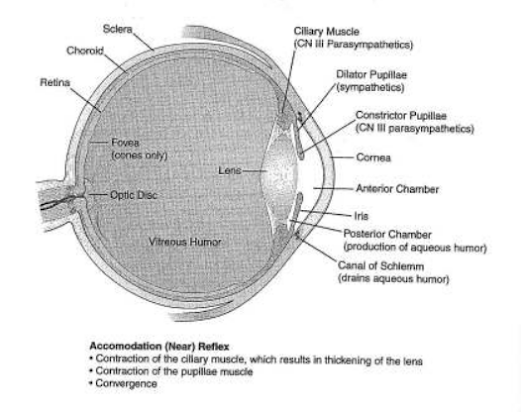 |
| Anatomy of Eyes |
Vitreous fluid: It is also known as vitreous Humour, it is a clear colorless jelly-like fluid between the lens and retina.
Lacrimal glands & ducts: Produce and drain tears.
Optic nerve: Nerve that carries visual impulse from the retina to the brain.
Conjunctiva: Mucous membrane lining the eyelids and anterior portion of the sclera.
Blepharitis: Inflammation of the eyelid.
Blepharoptosis: Drooping of the eyelid.
Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva.
Dacryocystitis: Inflammation of the tear sac.
Diplopia: Double vision.
Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea.
Ophthalmalgia: Pain in the eye.
Photophobia: Fear of light, sensitivity to light.
Cataract: Clouding of the lens of the eye.
Glaucoma: Increased intraocular tension.
Hyperopia: Farsightedness.
Myopia: Nearsightedness.
Nyctalopia: Poor vision at night.
Nystagmus: Involuntary, rhythmic movements of the eye.
Strabismus: Squint or crossed eyes.
Blepharoplasty: Surgical repair of the eyelid.
Iridectomy: Excision of part of the iris.
Keratoplasty: Surgical repair of the cornea.
Vitrectomy: Surgically removal of all or part of the vitreous fluid.
Ophthalmoscope: With a help of an instrument, visual examination of the eye.
Binocular: Pertaining to both eyes.
Intraocular: pertaining to within the eye.
Ophthalmologist: A physician who specializes in ophthalmology.
Optic: Pertaining to vision.
Optician: One who is skilled in filling prescriptions for lenses.
Retinopathy: Noninflammatory disease of the retina.
Miotic: An agent that constricts the pupil.
Mydriatic: An agent that dilates the pupil.
Dacryocyst: Lacrimal sac (tear sac)
Optometrist: A health professional who prescribes corrective lenses.
Visual Acuity: sharpness of vision of either distance or nearness.
Sense Organ - Ears
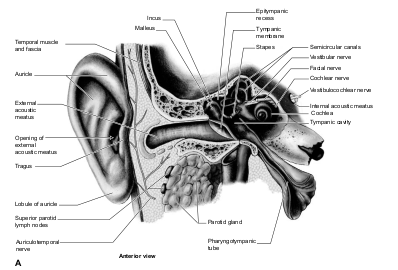 |
| Anatomy of Ear. |
Auricle/Pinna: The projecting shell-like structure on either side of the head.
Tympanic membrane: Eardrum, semitransparent membrane that separates the external meatus and the middle ear cavity.
 |
Tympanic Membrane |
Eustachian tube: It is a canal that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
Ossicles: Bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) of the middle ear, which carry sound vibrations.
Cochlea: Snail shaped, contains the organ of hearing.
Labyrinthitis: Inflammation of the labyrinth.
Mastoiditis: Inflammation of the mastoid bone.
Myringitis/Tympanitis: Inflammation of the eardrum.
Otalgia: Pain in the ear.
Otopyorrhea: Discharge of pus from the ear.
Meniere’s disease: Chronic disease of the inner ear, dizziness, and ringing in the ear.
Otitis externa: Inflammation of the outer ear.
Otitis media: Inflammation of the middle ear.
Tinnitus: Ringing in the ears.
Vertigo: Dizziness.
Labyrinthectomy: Excision of the labyrinth.
Mastoidectomy: Excision of the mastoid bone.
Myringoplasty: Surgical repair of the tympanic membrane.
Myringotomy: Surgical procedure to release the pus and relieve the pressure in the middle ear.
Tympanoplasty: Surgical repair of the eardrum.
Audiogram: Graphic record of the hearing.
Audiometry: Measurement of hearing.
Otoscopy: Visual examination of the ear.
Tympanometer: Instrument to measure middle ear functions.
Audiology: Study of hearing.
Audiologist: One who specializes in audiology.
Otology: Study of the ear.
Otorhinolaryngologist: An ENT physician who studies and treats diseases and disorders of the ear, nose, & throat.










0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in comment box.