 |
| Male reproductive system |
Reproductive / Genital System: A group of organs that work together for the purpose of reproduction.
Reproduction: A biological process by which individual organisms are produced. Though male and female reproductive systems are separate & unique, they both work together for the purpose of reproduction.
Functions of Reproductive System: The main function of the reproductive system is to ensure the survival of the species.
1. To produce gametes (eggs in female and sperm cells in a male)
2. To transport and nourish gametes
3. To nurture the developing offspring (embryo/fetus) in females.
4. To produce hormones that regulate the physiology of the reproductive system.
Internal genitalia: Genital organs that are located inside the body.
External genitalia: Genital organs that are located outside the body.
Functions of the Male Reproductive System:
1. To produce, nourish, and transport spermatozoon/sperm and semen.
2. To discharge the sperm within the female reproductive tract
3. To produce male sex hormones
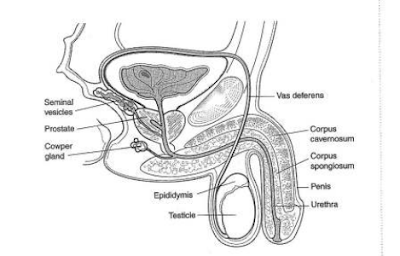
External Male Genitalia: Penis, scrotum, testes, and epididymis.
Internal Male Genitalia: Vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands.
Male Primary Reproductive Organs: Testes / Testicles.
Male Secondary Reproductive Organs: Ducts, glands, and penis.
Penis: A male organ for sexual intercourse, which conveys semen and urine. Three parts of the penis are the root, body/shaft, and glans/head. When a man reaches orgasm (sexual climax), semen, which contains sperm, is ejaculated through the end of the penis.
Glans penis: Cone-shaped end portion of the penis, covered with foreskin/prepuce.
Scrotum: Scrotum is a loose pouch-like sac of skin that hangs behind the penis. The scrotum contains testes and many nerves and blood vessels. The median septum divides the scrotum into 2 chambers. Each chamber houses a testis and an epididymis. Scrotum serves as a temperature regulator for testes. For normal sperm development, testes must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temp.
Muscles of Scrotum: Dartos Muscle and Cremaster Muscle
Testes / Testicles: Testes are paired oval organs that lie in the scrotum. Testes produce gametes (spermatozoon/sperm) and the primary male sex hormone (testosterone). Seminiferous tubules in testes are responsible for spermatogenesis.
Epididymis: A long coiled tube located at the backside of each testicle. Transports and stores sperm cells that are produced by the testes. Epididymis brings the sperm (immature) to maturity.
Vas deferens: Helps to transport the developed sperm to the urethra in preparation for ejaculation
Ejaculatory ducts: The ejaculatory ducts are formed by the fusion of vas deferens and seminal vesicles. The ejaculatory ducts enter into the urethra.
Urethra: Urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The urethra also expels semen when a man reaches orgasm.
Seminal vesicles: Seminal vesicles are sac-like pouches that are attached to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder. Seminal vesicles produce sugar-rich fluid (fructose) that provides energy to the sperm that helps in sperm's motility.
Prostate gland: Located below the urinary bladder, in front of the rectum. The prostate gland releases prostate fluid to help nourish the sperm.
Bulbourethral / Cowper's glands: Located on the sides of the urethra just below the prostate gland. Bulbourethral glands produce a clear, slippery fluid to lubricate the urethra and to neutralize any acidity.
Gamete: Sex or Reproductive cell. Sperm in males and Ovum in females.
Gonads: The reproductive organs that produce gametes.
Sperm: Sperm that emerge from testes is immature and incapable of fertilization.
Flagellum: Hair-like process in a sperm cell for motility purposes.
Ejaculation: Expulsion of sperm with fluid from the male urethra.
Testosterone: A primary male sex hormone secreted by the testes, which is responsible for male sex characteristics.
Semen: (prostatic and other glandular secretions)Spermatozoa and fluid.
Scrotum: Scrotum is a loose pouch-like sac of skin that hangs behind the penis. The scrotum contains testes and many nerves and blood vessels. The median septum divides the scrotum into 2 chambers. Each chamber houses a testis and an epididymis. Scrotum serves as a temperature regulator for testes. For normal sperm development, testes must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temp.
Muscles of Scrotum: Dartos Muscle and Cremaster Muscle
Testes / Testicles: Testes are paired oval organs that lie in the scrotum. Testes produce gametes (spermatozoon/sperm) and the primary male sex hormone (testosterone). Seminiferous tubules in testes are responsible for spermatogenesis.
Epididymis: A long coiled tube located at the backside of each testicle. Transports and stores sperm cells that are produced by the testes. Epididymis brings the sperm (immature) to maturity.
Vas deferens: Helps to transport the developed sperm to the urethra in preparation for ejaculation
Ejaculatory ducts: The ejaculatory ducts are formed by the fusion of vas deferens and seminal vesicles. The ejaculatory ducts enter into the urethra.
Urethra: Urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The urethra also expels semen when a man reaches orgasm.
Seminal vesicles: Seminal vesicles are sac-like pouches that are attached to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder. Seminal vesicles produce sugar-rich fluid (fructose) that provides energy to the sperm that helps in sperm's motility.
Prostate gland: Located below the urinary bladder, in front of the rectum. The prostate gland releases prostate fluid to help nourish the sperm.
Bulbourethral / Cowper's glands: Located on the sides of the urethra just below the prostate gland. Bulbourethral glands produce a clear, slippery fluid to lubricate the urethra and to neutralize any acidity.
Gamete: Sex or Reproductive cell. Sperm in males and Ovum in females.
Gonads: The reproductive organs that produce gametes.
Sperm: Sperm that emerge from testes is immature and incapable of fertilization.
Flagellum: Hair-like process in a sperm cell for motility purposes.
Ejaculation: Expulsion of sperm with fluid from the male urethra.
Testosterone: A primary male sex hormone secreted by the testes, which is responsible for male sex characteristics.
Semen: (prostatic and other glandular secretions)Spermatozoa and fluid.
Erectile Dysfunction: Inability to attain or maintain an erection sufficient for penile penetration (sexual intercourse)
Phimosis: Narrowing of the opening of the foreskin/prepuce
Coitus: Sexual intercourse
Puberty: When secondary sex characteristics develop
Cryptorchism / Cryptorchidism: Undescended testicles
Epispadias / Epispadias: Congenital opening of the male urethra on the upper surface of the penis
Hypospadias/Hypospadias: Congenital disorder. Where male urethra opens undersurface of the penis
Semen Analysis: A test done to determine fertility and effectiveness of vasectomy
Sterility: Men with fewer than 20 million sperm/mL are considered sterile. Fever or infection may cause temporary sterility.
Eunuch: When a male is castrated before puberty, he becomes a eunuch.
Balanitis: Inflammation of the glans penis.
Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate gland.
Prostatolith: Stone in the prostate gland.
Epididymitis: Inflammation of epididymis.
Hydrocele: Scrotal swelling (sac of clear fluid in the scrotum).
Spermatogenesis: Process of producing sperm cells.
Homosexual: Attracted to the same sex.
Heterosexual: Attracted to the opposite sex.
Aspermia: Absence of sperm
Oligospermia: Scanty sperm
Varicocele: Enlarged, swollen veins near the testicle
HPV: An STD. Benign cancerous growths in male & female genitals.
Syphilis: Chronic infectious disease caused by bacteria (spirochete). It can affect any part of the body.
Trichomoniasis: Infection of the genitourinary tract by Trichomonas
Chlamydial infection: Bacteria (Chlamydia trachomatis) invade the urethra in men and vagina and cervix in women. An STD.
Gonorrhea: Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genital tract, caused by bacteria (gonococci)
Carcinoma of testes: Malignant tumor of the testicles
Prostatic cancer: Cancer of the prostate gland
Ca of the prostate: Malignant tumor of the prostate gland
BPH: Nonmalignant excessive development of the prostate gland.
Prostatectomy: Excision of the prostate gland.
Hydrocelectomy: Surgical removal of a hydrocele.
Castration: Orchiectomy in males and oophorectomy in females.
Artificial insemination: Insertion of semen into the vagina by artificial means.
Sterilization: Any procedure providing an individual incapable of reproduction. ex: Vasectomy.
Circumcision: Removal of the foreskin/prepuce.
Vasectomy: Excision of a segment of the vas deferens (for sterilization).
Orchiectomy: Surgical removal of testis/testes.
Orchioplasty: Surgical repair of the testis/testes.
TUR/TURP: A resectoscope is inserted into the urethra and pieces of the prostate gland are removed by electrocautery or cryogenic techniques.
Pregnancy Test: Test to detect the level or presence of HCG in blood and Urine.
Gynecomastia: Excessive development of male mammary glands.
Mesosalpinx: The superior margin of the broad ligament that encloses the fallopian tube.
Perineorrhaphy: Surgical suturing of the perineum.
Perineum: the area between anus and scrotum in males; the area between anus and vulva in the female.
Fertilization / Conception: Union of sperm and ovum.
Menstruation: Cyclic endometrial shedding or discharge of bloody fluid from the uterus during the menstrual cycle.
Genitalia: The organs (internal and external) of reproduction or generation.
Oogenesis / Ovigenesis / Ovogenesis: Process of formation and development of the ovum.
Leukorrhea: white discharge (from the vagina).
Ectopic: out of place
Luteinization: Transformation of empty Graafian follicle into a corpus luteum after ovulation.
Menorrhagia: Abnormally heavy or prolonged menstruation, could lead to anemia.
The female reproductive system consists of: Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva (mons pubis, clitoris, external urethral meatus, Skene's glands, introitus, Bartholin glands, Labia Majora, Labia Minora).
Structural Division of Female Reproductive System:
1. Internal Female Genitalia - Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina
2. External Female Genitalia - Vulva / Pudendum
Functional Division of Female Reproductive System:
1. Primary reproductive organs - Ovaries
2. Secondary reproductive organs - Fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva.
Functions of the Female Reproductive System:
1. Produce and nourish female gametes (ovum/egg).
2. Transport gametes to a site where they may be fertilized by the sperm.
3. Provide a favorable environment for the developing fetus.
4. Deliver the fetus to the outside world once the development is completed.
5. Produce female sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone
Ovaries: Small oval / almond-shaped glands that are located on either side of the uterus. Ovaries are female gonads. They produce female gametes (ovum/egg) and hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
Ovarian ligaments: 1. Ovarian ligament. 2. Suspensory ligament. 3. Mesovarium
Ectopic: out of place
Luteinization: Transformation of empty Graafian follicle into a corpus luteum after ovulation.
Menorrhagia: Abnormally heavy or prolonged menstruation, could lead to anemia.
The female reproductive system consists of: Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva (mons pubis, clitoris, external urethral meatus, Skene's glands, introitus, Bartholin glands, Labia Majora, Labia Minora).
Structural Division of Female Reproductive System:
1. Internal Female Genitalia - Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina
2. External Female Genitalia - Vulva / Pudendum
 |
| Female Reproduction |
Functional Division of Female Reproductive System:
1. Primary reproductive organs - Ovaries
2. Secondary reproductive organs - Fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva.
Functions of the Female Reproductive System:
1. Produce and nourish female gametes (ovum/egg).
2. Transport gametes to a site where they may be fertilized by the sperm.
3. Provide a favorable environment for the developing fetus.
4. Deliver the fetus to the outside world once the development is completed.
5. Produce female sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone
Ovaries: Small oval / almond-shaped glands that are located on either side of the uterus. Ovaries are female gonads. They produce female gametes (ovum/egg) and hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
Ovarian ligaments: 1. Ovarian ligament. 2. Suspensory ligament. 3. Mesovarium
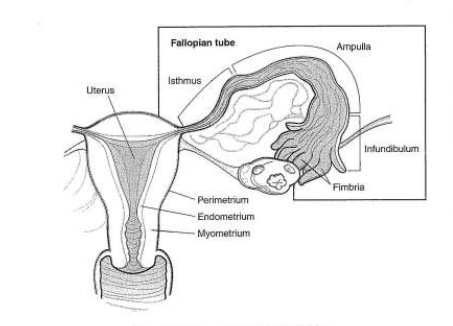
Fallopian tubes / Uterine tubes: Narrow muscular tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus. They transport ova from ovaries to the uterus. Conception/fertilization occurs in fallopian tubes. The fertilized ovum then moves to the uterus from fallopian tubes.
Parts of the fallopian tube: isthmus, ampulla (body), infundibulum, fimbriae, mesosalpinx.
Uterus/womb: A thick-walled, pear-shaped muscular chamber that acts as a home for a developing a fetus. The uterus is located in the pelvis anterior to the rectum and posterior to the urinary bladder.
Parts of uterus: fundus, corpus, isthmus, cervix.
Layers of the uterus: Uterine wall is made up of 3 layers. 1. Perimetrium. 2. Myometrium. 3. Endometrium
Parts of the fallopian tube: isthmus, ampulla (body), infundibulum, fimbriae, mesosalpinx.
Uterus/womb: A thick-walled, pear-shaped muscular chamber that acts as a home for a developing a fetus. The uterus is located in the pelvis anterior to the rectum and posterior to the urinary bladder.
Parts of uterus: fundus, corpus, isthmus, cervix.
Layers of the uterus: Uterine wall is made up of 3 layers. 1. Perimetrium. 2. Myometrium. 3. Endometrium
Uterine ligaments:
1. Broad ligaments (mesometrium).
2. Uterosacral ligament.
3. Round ligaments.
4. Cardinal (lateral cervical) ligaments
Vagina / Birth canal: A distensible muscular tube that connects the cervix to the outside of the body. It acts as an organ for copulation.
Receives a penis for intercourse. Acts as a passageway for the birth of a baby and also menstrual flow.
Vagina / Birth canal: A distensible muscular tube that connects the cervix to the outside of the body. It acts as an organ for copulation.
Receives a penis for intercourse. Acts as a passageway for the birth of a baby and also menstrual flow.
Hymen: A mucous membrane that partially covers the entrance of the vagina.
External female genitalia called as: Vulva / pudendum.
Clitoris: sensitive erectile organ or tissue positioned anterior to the vaginal orifice and in front of the urethral meatus. The clitoris creates sensations of pleasure during sexual intercourse.
Vestibule: The space between the labia minora that contains the vaginal and urethral openings.
Vestibular glands and types: Glands located around the vestibule and open into it. They secrete a fluid, which moistens and lubricates the vestibule. Types of vestibular glands: 1. Greater vestibular glands or Bartholin's glands. 2. Lesser vestibular glands or Skene's glands or paraurethral glands.
Breasts: Two mammaries (milk-producing) glands located in the upper anterior region of the chest.
Nipple (of the breast): Mammary papilla. A wart-like projection in the apex of each breast.
Areola: Dark pigmented area around the nipple.
Puberty: A natural phenomena in which the body moves into the adult phase, and capable of sexual reproduction. Puberty in females begins in early teens, generally between 11-14 years of age. At puberty, female gametes are released by gonads, sex hormones are secreted by gonads, and secondary sex characteristics are developed.
Puberty Vs Adolescence: Puberty: Limited to physical changes of sexual maturation. Adolescence: Psychological and social transition between childhood to adulthood.
Gonadotropins in women: FSH and LH.
Vestibule: The space between the labia minora that contains the vaginal and urethral openings.
Vestibular glands and types: Glands located around the vestibule and open into it. They secrete a fluid, which moistens and lubricates the vestibule. Types of vestibular glands: 1. Greater vestibular glands or Bartholin's glands. 2. Lesser vestibular glands or Skene's glands or paraurethral glands.
Breasts: Two mammaries (milk-producing) glands located in the upper anterior region of the chest.
Nipple (of the breast): Mammary papilla. A wart-like projection in the apex of each breast.
Areola: Dark pigmented area around the nipple.
Puberty: A natural phenomena in which the body moves into the adult phase, and capable of sexual reproduction. Puberty in females begins in early teens, generally between 11-14 years of age. At puberty, female gametes are released by gonads, sex hormones are secreted by gonads, and secondary sex characteristics are developed.
Puberty Vs Adolescence: Puberty: Limited to physical changes of sexual maturation. Adolescence: Psychological and social transition between childhood to adulthood.
Gonadotropins in women: FSH and LH.
Estrogen: It is a hormone produced by ovaries. Estrogen stimulates the development of secondary sex characteristics and prepares the uterus for pregnancy (endometrium gets thickened).
LH: A hormone produced by the pituitary gland. LH stimulates ovulation and luteinization.
LH: A hormone produced by the pituitary gland. LH stimulates ovulation and luteinization.
Menarche: First menstrual period i.e., the onset of the menstrual cycle.
Pubarche: First appearance of pubic hair in a child.
Thelarche: Onset of breast development.
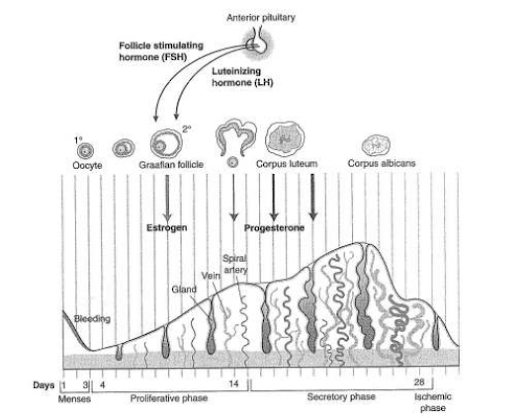
Menstrual cycle: Regular monthly reproductive cycle of a woman, the cycle lasts 28 days.
Phases of the menstrual cycle:
1. Menstrual phase - Days 1-5 - Period in which menstruation occurs (shedding of the uterine lining).
2. Proliferative phase - Days 6-13 - Period of endometrial repair.
3. Secretory phase - Days 14-28 - Period during which empty follicle develops into corpus luteum that secrets progesterone and estrogen.
Progesterone: It prepares the uterus for anembryo to implant.
Thelarche: Onset of breast development.
Menstrual cycle: Regular monthly reproductive cycle of a woman, the cycle lasts 28 days.
Phases of the menstrual cycle:
1. Menstrual phase - Days 1-5 - Period in which menstruation occurs (shedding of the uterine lining).
2. Proliferative phase - Days 6-13 - Period of endometrial repair.
3. Secretory phase - Days 14-28 - Period during which empty follicle develops into corpus luteum that secrets progesterone and estrogen.
 |
| Phase in Menstrual cycle |
Progesterone: It prepares the uterus for an
Menorrhagia: Abnormally heavy or prolonged menstruation, could lead to anemia.
Metrorrhagia: Irregular, acyclic, non-menstrual bleeding from the uterus, bleeding between periods (cause maybe ovarian/uterine cancer).
Menometrorrhagia: Irregular /excessive bleeding during menstruation and between menstrual periods.
Menopause: Permanent cessation of the menstrual cycle. This occurs between 45-50 years of age normally. After menopause, a woman is no longer considered to be fertile.
Fertilization/conception: Union of sperm and ovum.
Embryo: In humans, the developing organism from conception until the end of 8th week.
Fetus: The embryo from the 9th week until birth.
Perineum in woman / Pelvic floor: Area between anus and vagina.
Gestation: Pregnancy. Development of child from conception to birth, 9 months.
Orifice: An opening.
Ovulation: Ovary release egg(ovum).
Oocyte: Immature ovum
Introitus: External opening of the vagina.
Placenta: It serves as a communication between maternal and fetal bloodstreams. It is developed during pregnancy in the uterine wall.
Luteinization: Transformation of an empty Graafian follicle into a corpus luteum after ovulation.
Introitus: External opening of the vagina.
Placenta: It serves as a communication between maternal and fetal bloodstreams. It is developed during pregnancy in the uterine wall.
Luteinization: Transformation of an empty Graafian follicle into a corpus luteum after ovulation.
Coitus: Sexual intercourse / copulation / pareunia.
Ligation: Acting or binding. Tying.
Ligation: Acting or binding. Tying.
Cul-de-sac: A blind pouch between uterus and rectum.
Endometriosis: Endometrial tissue found in abnormal locations.
Fibroids: Benign tumors in the breasts.
Fibroids: Benign tumors in the breasts.
Ovarian cysts: Collection of fluid inside a sac in the ovary.
Ectopic pregnancy: Implantation of the fertilized egg in any other site other than normal location (uterus).
Imperforated hymen: A hymen that completely closes the external vaginal orifice. Menstrual flow cannot flow out of the body.
Pelvic exenteration: Removal of internal organs of the pelvis
Gamete: Sex cell; male - sperm & female - ovum / egg
Lactation: Process of milk production
Menorrhea: Menstruation (flow of blood from the uterus)
Oligomenorrhea: Scanty menstrual blood flow
Amenorrhea: Absence of normal menstrual flow (more than 3 months)
Dysmenorrhea: Painful menstruation (uterine pain during menstruation)
Oogenesis/ovigenesis: Process of formation and development of an ovum
Dyspareunia: Pain during sexual intercourse
Pyosalpinx: Distention of fallopian tube with pus
Oophoritis/ovaritis: Inflammation of an ovary.
Mastitis / mastadenitis: Inflammation of the breast.
Leukorrhea: White discharge from the vagina, indicates an infection or inflammation.
Galactorrhea: Abnormal white discharge (looks like milk) from the nipple in a non-breastfeeding woman. Continuous discharge of milk from the breasts between intervals of nursing in a breastfeeding woman.
Salpingorrhagia: Hemorrhage from the fallopian tube.
Cervicitis: Inflammation of the cervix.
Cystocele: Herniation of the bladder into the vagina.
Hysterectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus.
Hysterosalpingectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus and one or both fallopian tubes.
Hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy: Removal(surgically) of uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
Oophorectomy: Surgical removal of the ovary.
Salpingectomy: Surgical removal of the fallopian tube.
Salpingo-oophorectomy: Surgical removal of fallopian tube and ovary.
Mastectomy: Surgical removal of a breast.
Mammoplasty: Surgical repair of the breast.
Perineorrhaphy: Suture of ruptured perineum
Myomectomy/fibroidectomy: Surgical removal of uterine myoma.
Culdocentesis: Needle aspiration of fluid from the cul-de-sac.
Cauterization: Destruction of abnormal tissue with chemicals or electrically heated instruments.
Conization: Removal of a cone-shaped sample tissue for biopsy
Pap smear: Obtaining a smear of vaginal or cervical cells to screen for cervical cancer
Pregnancy test: Detect the presence of hCG(in blood or Urine).
Mammography: X-ray of female breasts
Aspiration: With help of a needle suction of fluid from a sac or cavity.
Ectopic pregnancy: Implantation of the fertilized egg in any other site other than normal location (uterus).
Imperforated hymen: A hymen that completely closes the external vaginal orifice. Menstrual flow cannot flow out of the body.
Pelvic exenteration: Removal of internal organs of the pelvis
Gamete: Sex cell; male - sperm & female - ovum / egg
Lactation: Process of milk production
Menorrhea: Menstruation (flow of blood from the uterus)
Oligomenorrhea: Scanty menstrual blood flow
Amenorrhea: Absence of normal menstrual flow (more than 3 months)
Dysmenorrhea: Painful menstruation (uterine pain during menstruation)
Oogenesis/ovigenesis: Process of formation and development of an ovum
Dyspareunia: Pain during sexual intercourse
Pyosalpinx: Distention of fallopian tube with pus
Oophoritis/ovaritis: Inflammation of an ovary.
Mastitis / mastadenitis: Inflammation of the breast.
Leukorrhea: White discharge from the vagina, indicates an infection or inflammation.
Galactorrhea: Abnormal white discharge (looks like milk) from the nipple in a non-breastfeeding woman. Continuous discharge of milk from the breasts between intervals of nursing in a breastfeeding woman.
Salpingorrhagia: Hemorrhage from the fallopian tube.
Cervicitis: Inflammation of the cervix.
Cystocele: Herniation of the bladder into the vagina.
Hysterectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus.
Hysterosalpingectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus and one or both fallopian tubes.
Hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy: Removal(surgically) of uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
Oophorectomy: Surgical removal of the ovary.
Salpingectomy: Surgical removal of the fallopian tube.
Salpingo-oophorectomy: Surgical removal of fallopian tube and ovary.
Mastectomy: Surgical removal of a breast.
Mammoplasty: Surgical repair of the breast.
Perineorrhaphy: Suture of ruptured perineum
Myomectomy/fibroidectomy: Surgical removal of uterine myoma.
Culdocentesis: Needle aspiration of fluid from the cul-de-sac.
Cauterization: Destruction of abnormal tissue with chemicals or electrically heated instruments.
Conization: Removal of a cone-shaped sample tissue for biopsy
Pap smear: Obtaining a smear of vaginal or cervical cells to screen for cervical cancer
Pregnancy test: Detect the presence of hCG(in blood or Urine).
Mammography: X-ray of female breasts
Aspiration: With help of a needle suction of fluid from a sac or cavity.
Aspiration biopsy: A technique for the evaluation of patients with breast disease.
Colposcopy: Visual examination of vagina and cervix.
Salpingoscopy: Visual examination of the fallopian tube
D&C: Widening of the cervix and scraping of the uterine cavity with a curette.
Parturition: Act of giving birth.
Premature infant: delivery of a baby before completing 37 weeks of gestation.
Puerperium: 6 weeks from the date of delivery of the baby.
Obstetrician: Physician who specializes in obstetrics.
Congenital anomaly: A defect that is present at the time of birth.
Breech birth: Expulsion of fetus where buttocks, feet, or knees emerge first to the outside world.
Antepartum: Occurring before childbirth.
Postpartum: Occurring after childbirth.
Gravida: Pregnant woman.
Intrapartum: Occurring during labor & delivery or childbirth.
Amniocentesis: Puncture to aspirate amniotic fluid, for assessment of fetal health & maturity, and aid in diagnosing fetal abnormalities.
Episiotomy: Incision of the perineum, during delivery to prevent tearing.
Spina bifida: Congenital defect in the vertebral column, failure of the vertebral arch to fuse.
Cleft lip & palate: A Congenital condition separation of the lip and roof of the mouth.
Pyloric stenosis: Narrowing of the pyloric sphincter.
Omphalocele: Herniation of intestine through the abdominal wall at the umbilicus.
Microcephaly: Fetus with a very small head.
Megacephaly/Macrocephaly: A condition, either congenital or acquired, in which the head is abnormally large.
Abortion: Termination of pregnancy, the expulsion of an embryo or a nonviable fetus from the uterus.
Hysterorrhexis: Rupture of the uterus.
Dystocia: Difficult labor.
Postpartum: Occurring after childbirth.
Gravida: Pregnant woman.
Intrapartum: Occurring during labor & delivery or childbirth.
Amniocentesis: Puncture to aspirate amniotic fluid, for assessment of fetal health & maturity, and aid in diagnosing fetal abnormalities.
Episiotomy: Incision of the perineum, during delivery to prevent tearing.
Spina bifida: Congenital defect in the vertebral column, failure of the vertebral arch to fuse.
Cleft lip & palate: A Congenital condition separation of the lip and roof of the mouth.
Pyloric stenosis: Narrowing of the pyloric sphincter.
Omphalocele: Herniation of intestine through the abdominal wall at the umbilicus.
Microcephaly: Fetus with a very small head.
Megacephaly/Macrocephaly: A condition, either congenital or acquired, in which the head is abnormally large.
Abortion: Termination of pregnancy, the expulsion of an embryo or a nonviable fetus from the uterus.
Hysterorrhexis: Rupture of the uterus.
Dystocia: Difficult labor.
Amniotic sac: Membranous bag that surrounds the fetus before delivery.
Amniotic fluid: Fluid within the amniotic sac.
Placenta previa: Placenta is placed in the lower segment of the uterus.
Primigravida: Woman in her first pregnancy.
Nulligravida: Woman who never has given birth.
Multigravida: Woman who has given birth many times.










0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in comment box.