Epidural Steroid injection:-
What is an epidural steroid injection?
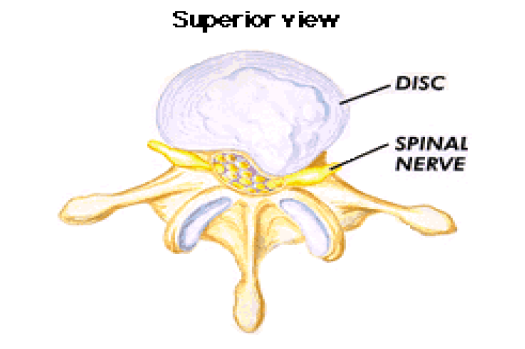
An epidural steroid injection is a common procedure to treat spinal nerve irritation that causes chronic low back pain and/or leg pain (radicular pain). Disc herniation is also treated with epidural steroid injections. Epidural injections are also used to treat nerve compression in the neck (cervical radiculopathy). The procedure is quick and simple.
Sample Report:
1-REASON: c-spine injection
P 77002 FL GUIDE NDL PLACE
RESULT: Left radiculopathy
Under sterile precautions and using CT guidance, a 24-gauge needle was inserted into the epidural space at the C6-C7 intervertebral space. Once the position of the needle was insure in the epidural space 80 mg of methylprednisolone was injected into the epidural space at the level of C6-C7. The patient tolerated the procedure well. No complications occurred
IMPRESSION: Successful epidural injection of methylprednisone into the cervical spine.
TECHNIQUE: Following the acquisition of informed consent, the patient was placed in the prone position on the table and site selected over the L4-5 interlaminar space for appropriate ESI to follow under fluoroscopic guidance. A mark was placed on the patient's skin with an indelible marker and the patient was prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. Thereafter, 1% lidocaine solution was utilized for local anesthetic effect. A 20-gauge Chiba needle was advanced into the epidural space without difficulty. Epidurogram was performed with an injection of 0.3 ml of Isovue-300. This revealed a normal-appearing epidurogram. Thereafter, 120 mg of Depo- Medrol mixed with 1.5 mL of 0.25% bupivacaine and 0.5 mL of sterile saline. This was injected without difficulty. At the conclusion of the procedure, the needle was withdrawn and pressure was held on the site until all appreciable bleeding subsided. A bandage was placed on the site. The patient left the department in good condition.
IMPRESSION: 1. Successful lumbar ESI at L4-5. 2. This is the patient's first injection in this series.
1-REASON: c-spine injection
P 77002 FL GUIDE NDL PLACE
RESULT: Left radiculopathy
Under sterile precautions and using CT guidance, a 24-gauge needle was inserted into the epidural space at the C6-C7 intervertebral space. Once the position of the needle was insure in the epidural space 80 mg of methylprednisolone was injected into the epidural space at the level of C6-C7. The patient tolerated the procedure well. No complications occurred
IMPRESSION: Successful epidural injection of methylprednisone into the cervical spine.
2-LUMBAR ESI UNDER FLUOROSCOPIC GUIDANCE
INDICATION: Herniated disc.
COMPARISON: None.
INDICATION: Herniated disc.
COMPARISON: None.
TECHNIQUE: Following the acquisition of informed consent, the patient was placed in the prone position on the table and site selected over the L4-5 interlaminar space for appropriate ESI to follow under fluoroscopic guidance. A mark was placed on the patient's skin with an indelible marker and the patient was prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. Thereafter, 1% lidocaine solution was utilized for local anesthetic effect. A 20-gauge Chiba needle was advanced into the epidural space without difficulty. Epidurogram was performed with an injection of 0.3 ml of Isovue-300. This revealed a normal-appearing epidurogram. Thereafter, 120 mg of Depo- Medrol mixed with 1.5 mL of 0.25% bupivacaine and 0.5 mL of sterile saline. This was injected without difficulty. At the conclusion of the procedure, the needle was withdrawn and pressure was held on the site until all appreciable bleeding subsided. A bandage was placed on the site. The patient left the department in good condition.
IMPRESSION: 1. Successful lumbar ESI at L4-5. 2. This is the patient's first injection in this series.










0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in comment box.