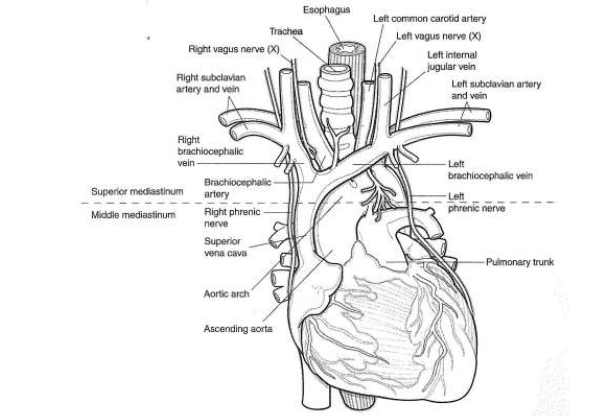
 |
| Structure of the Mediastinum |
Cardiovascular System: Group of organs that circulate blood in the human body.
The function of blood circulation: Blood circulation provides O2 and nutrients to cells and removes CO2 and waste material from cells.
Organs of Cardiovascular System: Heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Heart: The heart is a 4-chambered, fist-sized, hollow muscular organ that pumps blood into the blood vessels by repeated contractions. The heart is positioned in the mediastinum, between the lungs.
Chambers of the heart: There is a total of 4 chambers (2 atria & 2 ventricles) in the human body.
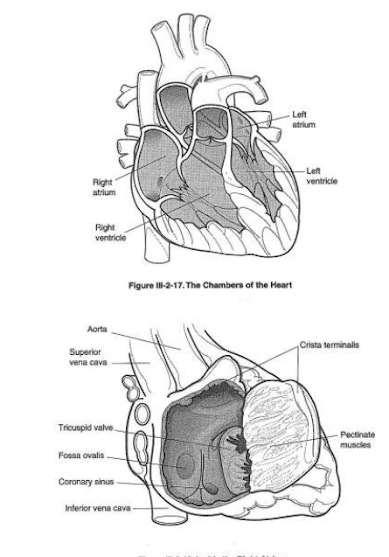 |
| Four chamber Heart |
Base and apex of the heart: Broad superior portion of the heart is base and the narrow inferior portion of the heart is the apex.
Atria: Atria is the upper receiving chambers. They are Right Atrium and Left Atrium.
Right Atrium: The right upper chamber (right atrium) receives blood from all body parts except the lungs. The superior and inferior vena cavae (2 larger veins) bring deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
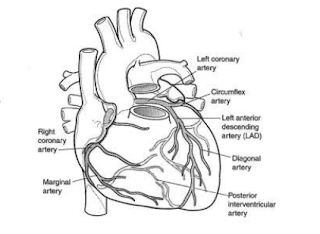 |
| Arterial supply of heart |
Left Atrium: The left upper chamber (left atrium) receives blood from the lungs. Left and right pulmonary veins bring oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
Atrial Septum: The partition between right and left atria.
Ventricles: Ventricles are the lower receiving chambers. They are the Right Ventricle and Left Ventricle.

Right Ventricle: The right lower chamber (right ventricle) receives the blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs through the pulmonary artery for purification.
Left Ventricle: The left lower chamber (left ventricle) receives the blood from the left atrium and pumps it to the aorta.
Ventricular Septum: The partition between the right and left ventricles.
The largest artery in the human body: Aorta.
Valve: A structure in a hollow organ that maintains the unidirectional flow of fluid.
Heart valves: The heart has 4 valves.
1. Tricuspid / Right Atrioventricular valve
2. Bicuspid / Mitral / Left Atrioventricular valve
3. Pulmonary valve
4. Aortic valve
Tricuspid / right atrioventricular valve: Located between the right atrium and right ventricle. It allows the unidirectional flow of blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
Bicuspid/mitral/left atrioventricular valve: It is located between the left atrium and left ventricle. It allows the unidirectional flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
Pulmonary valve: Located at the beginning portion of the pulmonary artery that starts from the right ventricle. It allows the unidirectional flow of blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Aortic valve: Located at the beginning of the aorta that starts from the left ventricle. It allows the unidirectional flow of blood from the left ventricle to the aorta.
Semilunar valves: Both pulmonary and aortic valves combinedly called Semilunar valves.
Layers of the heart wall: Endocardium (inner lining), Myocardium (middle thick muscular layer), and Pericardium (2-layered sac covering the heart).
Pericardial layers: Visceral pericardium (inner layer) and parietal pericardium (outer layer).
Pericardial cavity: The space between the visceral and parietal pericardial is the pericardial cavity.
Pericardial fluid: Pericardial cavity contains a fluid called pericardial fluid, which lubricates the membranes.
Coronary Circulation: Coronary circulation means the heart has its own vascular system to provide O2 and nutrients to the heart muscle. It consists of coronary arteries and coronary veins.
The function of the coronary arteries and coronary veins: Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart. Coronary veins drain the blood from the heart into the right atrium.
Main coronary veins: Besian Vein, Great Cardiac Vein, Middle Cardiac Vein, Left Marginal Vein, Coronary Sinus
Coronary arteries:
Right Coronary Artery (RCA): Right marginal, posterior interventricular (descending) branch
Left Coronary Artery (LCA): Left anterior interventricular (descending) artery, circumflex artery
Heart's conduction system: The system that generates electrical impulses required for a heartbeat and distributes them among heart muscle.
Main coronary veins: Besian Vein, Great Cardiac Vein, Middle Cardiac Vein, Left Marginal Vein, Coronary Sinus
Coronary arteries:
Right Coronary Artery (RCA): Right marginal, posterior interventricular (descending) branch
Left Coronary Artery (LCA): Left anterior interventricular (descending) artery, circumflex artery
Heart's conduction system: The system that generates electrical impulses required for a heartbeat and distributes them among heart muscle.
Parts of the Conduction system of heart:
1. Sinoatrial Node (SA node)
2. Atrioventricular Node (AV node)
3. Bundle of His
4. Right and Left Bundle Branches
5. Purkinje Fibers.
 |
| Cardiac conduction system |
Heartbeat: Act of contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Systole: Ventricular contraction.
Diastole: Ventricular relaxation.
Heart sounds: Sounds that are produced during the closure of the heart valve.
S1 and S2 sound:
S1 (First Heart Sound) - LUBB - occurs with the closure of AV valves, i.e., tricuspid and bicuspid valves.
S2 (Second Heart Sound) - DUPP - occurs with the closure of semilunar valves, i.e., pulmonary and aortic valves.
Auscultation: Listening to the sounds made by the body organs.
Where do you feel radial pulse: Radial pulse is felt on the wrist, just under the thumb.
Arterial pulses in the human body: Temporal, Carotid, Brachial, Radial, Femoral, Popliteal, and Dorsalis Pedis.
Major blood vessels in the human body are: Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries.
Arteries: Large blood vessels that carry oxygenated (pure) blood away from the heart to the body cells. Blood pressure is much in the arteries.
Arterioles: Small branches of arteries are called Arterioles.
Veins: Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated (impure) blood from tissues to the heart. Blood pressure is low in veins.
Venules: Small branches of veins are called Venules.
Capillaries: Capillaries are microscopic blood vessels, which connect arterioles and venules.
Blood Pressure (BP) and how it is measured: The force exerted by the blood on the arterial walls. BP is measured with the help of a Sphygmomanometer (arterial BP). BP has systolic and diastolic pressure values.
Veins: Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated (impure) blood from tissues to the heart. Blood pressure is low in veins.
Venules: Small branches of veins are called Venules.
Capillaries: Capillaries are microscopic blood vessels, which connect arterioles and venules.
Blood Pressure (BP) and how it is measured: The force exerted by the blood on the arterial walls. BP is measured with the help of a Sphygmomanometer (arterial BP). BP has systolic and diastolic pressure values.
Ex: 120/80. 120 - Systolic pressure &
80 - Diastolic pressure
Largest veins in the human body and their function: Superior and Inferior vena cavae. The inferior vena cava brings the blood from below the diaphragm and the superior vena cava brings blood from the upper parts of the body.
Cardiovascular circuit: Loop made up of heart and blood vessels that carry blood through the body and back to the heart.
Pulmonary circuit: Pulmonary circuit made up of the Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Trunk, Pulmonary Arteries, Lungs, Pulmonary Veins, and Left Atrium. Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart.
The systemic circuit made up of the Left Ventricle, Aorta and its branches, Superior and Inferior vena cavae, and Right Atrium. Systemic circulation supplies oxygenated blood to all the body parts except the lungs.
Embolus: An object (other than blood components) that travels through the bloodstream, lodges in a blood vessel and blocks it.
Claudication: Tiredness or pain in the arms and legs caused by inadequate oxygen supply to the muscles, usually due to narrowed arteries.
Palpitation: An uncomfortable sensation in the chest caused by an irregular heartbeat, perceptible to the patient
Murmur: An extra or unusual heart sound heard along with heartbeat.
Stent: A device made up of expandable metal mesh placed at the site of a narrowed artery.
Syncope: Temporary loss of consciousness.
Cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of the skin due to insufficient oxygen in the blood.
Dyspnea: Shortness of breath
Dextrocardia: Location of the heart on the right side of the chest.
Myocardial: Location of the heart in the more central portion of the chest.
Edema: Swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the body tissues.
Pallor: Pale color of the skin due to the reduced amount of oxyhemoglobin.
Plaque: Fatty deposit in the inner lining of the arterial wall.
Sick Sinus Syndrome (SSS): Failure of the sinus node (SA node) to regulate the heart's rhythm.
Silent ischemia: An episode of cardiac ischemia not accompanied by chest pain.
Stenosis: Narrowing/constriction of an opening.
Thrombus: A blood clot.
Thrombolysis: Dissolution (breaking up) of a blood clot.
Vertigo: A feeling of dizziness/spinning.
Arrhythmia/dysrhythmia: Abnormal heart rate and/or rhythm. If there is any abnormality in the conduction system of the heart, arrhythmia will occur.
Sinus Bradycardia: Abnormally slow heart rate (less than 60 beats/min) due to malfunction of SA node.
Heart block and types: Slowed or disrupted conduction of electrical signals throughout the heart. Types: 1. Partial heart block. 2. Complete heart block.
Treatment for bradycardias: Treated by inserting an artificial pacemaker.
Largest veins in the human body and their function: Superior and Inferior vena cavae. The inferior vena cava brings the blood from below the diaphragm and the superior vena cava brings blood from the upper parts of the body.
Cardiovascular circuit: Loop made up of heart and blood vessels that carry blood through the body and back to the heart.
Pulmonary circuit: Pulmonary circuit made up of the Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Trunk, Pulmonary Arteries, Lungs, Pulmonary Veins, and Left Atrium. Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart.
The systemic circuit made up of the Left Ventricle, Aorta and its branches, Superior and Inferior vena cavae, and Right Atrium. Systemic circulation supplies oxygenated blood to all the body parts except the lungs.
Embolus: An object (other than blood components) that travels through the bloodstream, lodges in a blood vessel and blocks it.
Claudication: Tiredness or pain in the arms and legs caused by inadequate oxygen supply to the muscles, usually due to narrowed arteries.
Palpitation: An uncomfortable sensation in the chest caused by an irregular heartbeat, perceptible to the patient
Murmur: An extra or unusual heart sound heard along with heartbeat.
Stent: A device made up of expandable metal mesh placed at the site of a narrowed artery.
Syncope: Temporary loss of consciousness.
Cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of the skin due to insufficient oxygen in the blood.
Dyspnea: Shortness of breath
Dextrocardia: Location of the heart on the right side of the chest.
Myocardial: Location of the heart in the more central portion of the chest.
Edema: Swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the body tissues.
Pallor: Pale color of the skin due to the reduced amount of oxyhemoglobin.
Plaque: Fatty deposit in the inner lining of the arterial wall.
Sick Sinus Syndrome (SSS): Failure of the sinus node (SA node) to regulate the heart's rhythm.
Silent ischemia: An episode of cardiac ischemia not accompanied by chest pain.
Stenosis: Narrowing/constriction of an opening.
Thrombus: A blood clot.
Thrombolysis: Dissolution (breaking up) of a blood clot.
Vertigo: A feeling of dizziness/spinning.
Arrhythmia/dysrhythmia: Abnormal heart rate and/or rhythm. If there is any abnormality in the conduction system of the heart, arrhythmia will occur.
Sinus Bradycardia: Abnormally slow heart rate (less than 60 beats/min) due to malfunction of SA node.
Heart block and types: Slowed or disrupted conduction of electrical signals throughout the heart. Types: 1. Partial heart block. 2. Complete heart block.
Treatment for bradycardias: Treated by inserting an artificial pacemaker.
Artificial pacemaker: A device that is implanted in the chest to monitor and correct the arrhythmias, mainly bradycardia.
It has 2 parts: 1. Pulse generator. 2. Electrode leads.
Bradycardia: (less than 60 beats/min).-Slow Heart rate
Tachycardia: (more than 100 beats/min.)-Rapid Heart rate
Bradycardia: (less than 60 beats/min).-Slow Heart rate
Tachycardia: (more than 100 beats/min.)-Rapid Heart rate
Flutter: Rapid, regular heart rate of around 300 beats/min. Types: Atrial flutter, Ventricular flutter.
Fibrillation: Rapid, irregular, ineffective heart rate of around 350 beats/min.
Examples: Atrial fibrillation, Ventricular fibrillation.
Treatment for tachycardias: Treated by placing ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator)
ICD: A device that is implanted in the chest to constantly monitor and correct the arrhythmias, mainly tachycardias. ICD delivers a jolt to reset the heart rate.
Coronary Artery Disease / Coronary Atherosclerosis: It occurs when there is a build-up of cholesterol-rich plaque along the lining of coronary arteries.
Treatment for tachycardias: Treated by placing ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator)
ICD: A device that is implanted in the chest to constantly monitor and correct the arrhythmias, mainly tachycardias. ICD delivers a jolt to reset the heart rate.
Coronary Artery Disease / Coronary Atherosclerosis: It occurs when there is a build-up of cholesterol-rich plaque along the lining of coronary arteries.
Ischemia: Decreased blood flow to the heart muscle
Myocardial Infarction (MI) / Heart attack: Death of heart muscle when the blood flow is completely blocked. The symptom of MI: Angina (chest pain).
Diagnosis and treatment of CAD:
Diagnosis: EKG, TMT, Coronary Angiography
Treatment: PTCA, CABG
Coronary angiography: A contrast material (dye) is injected into the coronary arteries and x-rays are taken to study the blood circulation through the vessels.
Coronary angioplasty: A nonsurgical treatment by inflating a tiny balloon inside the coronary artery and placing a stent.
CABG: A surgical rerouting of blood around a deceased (dead) vessel. A small piece of vein from the leg is used for grafting.
Valvular stenosis: Narrowing of the orifice of the valve. Ex: Mitral stenosis, tricuspid stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, and aortic stenosis.
Valvular prolapse: Improper closure of a valve. Ex: Mitral valve prolapse, Tricuspid valve prolapse.
Regurgitation: Leakage or backflow of blood. Ex: Mitral regurgitation
Myocardial Infarction (MI) / Heart attack: Death of heart muscle when the blood flow is completely blocked. The symptom of MI: Angina (chest pain).
Diagnosis and treatment of CAD:
Diagnosis: EKG, TMT, Coronary Angiography
Treatment: PTCA, CABG
Coronary angiography: A contrast material (dye) is injected into the coronary arteries and x-rays are taken to study the blood circulation through the vessels.
Coronary angioplasty: A nonsurgical treatment by inflating a tiny balloon inside the coronary artery and placing a stent.
CABG: A surgical rerouting of blood around a deceased (dead) vessel. A small piece of vein from the leg is used for grafting.
Valvular stenosis: Narrowing of the orifice of the valve. Ex: Mitral stenosis, tricuspid stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, and aortic stenosis.
Valvular prolapse: Improper closure of a valve. Ex: Mitral valve prolapse, Tricuspid valve prolapse.
Regurgitation: Leakage or backflow of blood. Ex: Mitral regurgitation
Congenital Heart disease: Abnormalities or malformations of heart present at the time of birth.
Coarctation of the aorta: Narrowing of the aorta (congenital)
Septal defect: Small holes between septa or ventricles. Ex: Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) and Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
Tetralogy of Fallot: A congenital malformation of the heart involving 4 distinct defects (Pulmonary stenosis, VSD, Overriding of the aorta, or shift of aorta to the right, and hypertrophy of the right ventricle).
Varicose veins: Abnormally swollen and twisted veins, usually in the legs.
Aneurysm: A balloon-like bulge in an artery resulting from the weakening of the arterial wall.
Congestive Heart Failure: Insufficient ventricular ejection due to weakened heart muscle.
Bacterial endocarditis: Infection and inflamation of the inner lining of the heart and heart valve caused by bacteria.
Deep Vein Thrombosis: A blood clot in a deep vein (in calf, thigh, arm, or pelvis)
Pericardial effusion: Accumulation of fluid in the pericardium.
Cardiac Arrest: Sudden stoppage of the heartbeat.
PACs: Early contractions of atria, caused by impulses generated by ectopic foci.
PVCs: Early contractions of ventricles, caused by impulses generated by ectopic foci.
Angina pectoris: Chest pain due to ischemia or infarction.
Rheumatic Heart Disease: Damage of heart valves due to rheumatic fever.
Hypertension: High blood pressure
Hypotension: Low blood pressure.
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD): Blockage of arteries in the lower extremities due to atherosclerosis.
Holter monitor: A portable device to record the heartbeats over a period of 24 hours or more.
Anticoagulants: Drugs used to prevent blood clotting. Ex: Heparin
Antihypertensive drugs: Drugs used to lower BP. Ex: Calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers.
Thrombolytics: Drugs used to dissolve blood clots.
Diuretics: Drugs used to lower BP by stimulating fluid loss (promoting urine production)
Digitalis: Drugs used to increase the strength and regularity of the heartbeat.
Nitrates: Drugs used to treat angina. Nitrates can dilate the coronary arteries so that blood flow can be increased, to reduce the risk of ischemia.
Hypertensive heart disease: A disorder of the heart resulting from high BP.
Rheumatic fever: An inflammatory disease that occurs in children.
Venipuncture: Puncture of a vein to remove blood for testing, installing meds, etc.
Percussion: Tapping on the body surface.
Heart murmur: A short-duration humming sound of cardiac origin.
Cardiac catheterization: Introduction of a catheter into the heart through a blood vessel to determine the cardiac disease.
Stethoscope: An instrument used to examine the chest sounds.
Defibrillation / Cardioversion: A technique of applying an electrical shock (jolt) to the chest in order to covert an abnormal heart rhythm to normal. The device which performs Defibrillation / Cardioversion is called Defibrillator / Cardioverter.
Angiostenosis / Angiospasm: Narrowing of a blood vessel
Aortic stenosis: Narrowing of the aorta
Arteriorrhexis: Rupture of an artery
Arteriosclerosis: Hardening of the arteries
Cardiodynia: Pain in the heart
Cardiomegaly: Enlargement of the heart
Cardiomyopathy: Disease condition of the heart muscle
Cardiovalvulitis: Inflammation of the heart valves
Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle (middle layer of the heart)
Angiography: Suturing of a blood vessel
Angioplasty: Surgical repair of a blood vessel
Endarterectomy: Excision within of the thickened inferior of an artery
Atherectomy: Surgical removal of a plaque
Aneurysmectomy: Surgical excision of an aneurysm
Embolectomy: Surgical removal of an embolus (clot).
Angioscope: An instrument for visual examination of a blood vessel
Angiography: X-ray filming of a blood vessel.
Vasodilator: An agent that causes dilatation of the blood vessels.
Vasoconstrictor: An agent that causes narrowing of the blood vessels.
Extravasation: Leakage of blood from the blood vessel into the tissue.
Angiocarditis: Inflammation of the blood vessels and heart
Echocardiography: The use of ultrasound in the investigation of the heart and great vessels
Doppler Flow Study: An ultrasound study to determine the velocity of the flow of blood within the vessels.
Ischemia: Reduced blood supply (local anemia) to an organ or body part due to mechanical obstruction like arterial narrowing or disruption.
Coarctation of the aorta: Narrowing of the aorta (congenital)
Septal defect: Small holes between septa or ventricles. Ex: Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) and Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
Tetralogy of Fallot: A congenital malformation of the heart involving 4 distinct defects (Pulmonary stenosis, VSD, Overriding of the aorta, or shift of aorta to the right, and hypertrophy of the right ventricle).
Varicose veins: Abnormally swollen and twisted veins, usually in the legs.
Aneurysm: A balloon-like bulge in an artery resulting from the weakening of the arterial wall.
Congestive Heart Failure: Insufficient ventricular ejection due to weakened heart muscle.
Bacterial endocarditis: Infection and inflamation of the inner lining of the heart and heart valve caused by bacteria.
Deep Vein Thrombosis: A blood clot in a deep vein (in calf, thigh, arm, or pelvis)
Pericardial effusion: Accumulation of fluid in the pericardium.
Cardiac Arrest: Sudden stoppage of the heartbeat.
PACs: Early contractions of atria, caused by impulses generated by ectopic foci.
PVCs: Early contractions of ventricles, caused by impulses generated by ectopic foci.
Angina pectoris: Chest pain due to ischemia or infarction.
Rheumatic Heart Disease: Damage of heart valves due to rheumatic fever.
Hypertension: High blood pressure
Hypotension: Low blood pressure.
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD): Blockage of arteries in the lower extremities due to atherosclerosis.
Holter monitor: A portable device to record the heartbeats over a period of 24 hours or more.
Anticoagulants: Drugs used to prevent blood clotting. Ex: Heparin
Antihypertensive drugs: Drugs used to lower BP. Ex: Calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers.
Thrombolytics: Drugs used to dissolve blood clots.
Diuretics: Drugs used to lower BP by stimulating fluid loss (promoting urine production)
Digitalis: Drugs used to increase the strength and regularity of the heartbeat.
Nitrates: Drugs used to treat angina. Nitrates can dilate the coronary arteries so that blood flow can be increased, to reduce the risk of ischemia.
Hypertensive heart disease: A disorder of the heart resulting from high BP.
Rheumatic fever: An inflammatory disease that occurs in children.
Venipuncture: Puncture of a vein to remove blood for testing, installing meds, etc.
Percussion: Tapping on the body surface.
Heart murmur: A short-duration humming sound of cardiac origin.
Cardiac catheterization: Introduction of a catheter into the heart through a blood vessel to determine the cardiac disease.
Stethoscope: An instrument used to examine the chest sounds.
Defibrillation / Cardioversion: A technique of applying an electrical shock (jolt) to the chest in order to covert an abnormal heart rhythm to normal. The device which performs Defibrillation / Cardioversion is called Defibrillator / Cardioverter.
Angiostenosis / Angiospasm: Narrowing of a blood vessel
Aortic stenosis: Narrowing of the aorta
Arteriorrhexis: Rupture of an artery
Arteriosclerosis: Hardening of the arteries
Cardiodynia: Pain in the heart
Cardiomegaly: Enlargement of the heart
Cardiomyopathy: Disease condition of the heart muscle
Cardiovalvulitis: Inflammation of the heart valves
Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle (middle layer of the heart)
Angiography: Suturing of a blood vessel
Angioplasty: Surgical repair of a blood vessel
Endarterectomy: Excision within of the thickened inferior of an artery
Atherectomy: Surgical removal of a plaque
Aneurysmectomy: Surgical excision of an aneurysm
Embolectomy: Surgical removal of an embolus (clot).
Angioscope: An instrument for visual examination of a blood vessel
Angiography: X-ray filming of a blood vessel.
Vasodilator: An agent that causes dilatation of the blood vessels.
Vasoconstrictor: An agent that causes narrowing of the blood vessels.
Extravasation: Leakage of blood from the blood vessel into the tissue.
Angiocarditis: Inflammation of the blood vessels and heart
Echocardiography: The use of ultrasound in the investigation of the heart and great vessels
Doppler Flow Study: An ultrasound study to determine the velocity of the flow of blood within the vessels.
Ischemia: Reduced blood supply (local anemia) to an organ or body part due to mechanical obstruction like arterial narrowing or disruption.










0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in comment box.